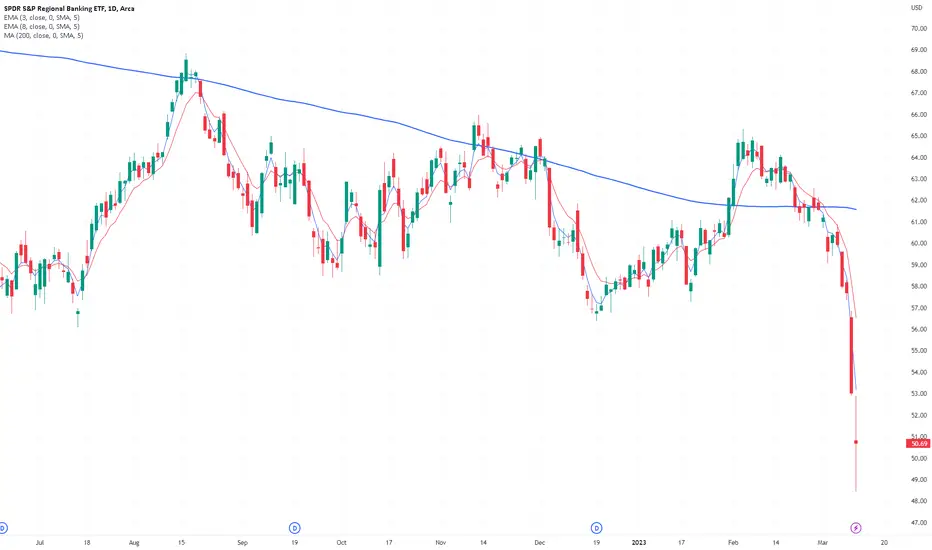
A lot of talk on who is to blame for the SVB Financial collapse – this is the first big casualty of rapid rate hikes and tighter policy, but who is to blame and what are the next steps?
-SVBs management – they invested short-term deposits in longer term fixed income assets – where a large % of its $120b securities portfolio lacked any kind of interest rate hedge (payers swaps were clearly needed)
-SVBs management – In the past 8 months SVB had no risk manager - fortune.com/2023/03/10/silicon-valley-bank-chief-risk-officer/ - no one knows how they efficiently managed risk
-SVBs management – the accounts showed they held $91b of its $120b securities in its HTM (assets Held to Maturity) book – these are assets they intend to hold until maturity but the accounting rules detail, that they don’t need to mark-to-market the moves in the underlying and report the ballooning losses – which again were not hedged.
-SVB deposit mix - 93%+ were above the FDIC insurance limit – this makes depositors v sensitive to any capital concerns at the bank
-SVB deposit mix - VCs had a rapid cash burn, as projects they back are typically driven by changes in interest rates (think Net Present value and Internal rates of return) – depositors took cash off SVB’s balance sheet to fund operations – SVB subsequently had to sell assets as their liabilities fell – we then see realised losses from buying securities at much higher prices.
-Short sellers/investor base – shorts had an eye on unrealised losses from the worsening asset quality for weeks – the selling accelerated when the CEO/CFO/CMO disclosed they’d sold a chunk of stock on 27 March – it was over when the SVB took a $1.8b hit on its AFS securities available for sale on Wednesday – management sold $21b of its $28b book and announced a $2.25b in equity/debt raising - investors knew with conviction that depositors were fleeing – who supports a raising when liabilities are falling – no one sensible, raising pulled
-The Fed - failing to know such a shift in rates would impact banks asset quality when its primary function is financial stability.
-Regulation - Basel 3 - banks being forced to buy govt paper against deposits - v low risk weighting (perhaps required a hedge
Hard to pinpoint this on one aspect IMO - I think there is a perfect storm going on – a lack of hedging of interest rate risk was clearly a dominant factor behind this. Top down this is a function of rapidly tightening monetary policy and the impact this had on both the asset quality and liability side of the balance sheet – we should recall SVBs model is not the same as others in the banking space, so its hard to say this is systemic – still we wait for the outcome on next steps on how deposits over $250k will be dealt with – we’re hearing they may get 50% back initially but a buyer would be the best solution
The issue for regional/smaller banks comes if is we see some sort of haircut on the deposits claim over $250k – that could see a loss of confidence in holding deposits with other smaller banks names – we shall hear more soon, but broad contagion through the financial system seems unlikely, but it is a possibility given nearly 1/3 deposits in the banking system are uninsured – any bank with a large asset base and low equity are in the spotlight
As said Friday this could be a nothing burger or have real impactions on economics - the big issue happens this week if we see no clarity on how depositors are dealt (seems unlikely) with and we get a hot CPI print
-SVBs management – they invested short-term deposits in longer term fixed income assets – where a large % of its $120b securities portfolio lacked any kind of interest rate hedge (payers swaps were clearly needed)
-SVBs management – In the past 8 months SVB had no risk manager - fortune.com/2023/03/10/silicon-valley-bank-chief-risk-officer/ - no one knows how they efficiently managed risk
-SVBs management – the accounts showed they held $91b of its $120b securities in its HTM (assets Held to Maturity) book – these are assets they intend to hold until maturity but the accounting rules detail, that they don’t need to mark-to-market the moves in the underlying and report the ballooning losses – which again were not hedged.
-SVB deposit mix - 93%+ were above the FDIC insurance limit – this makes depositors v sensitive to any capital concerns at the bank
-SVB deposit mix - VCs had a rapid cash burn, as projects they back are typically driven by changes in interest rates (think Net Present value and Internal rates of return) – depositors took cash off SVB’s balance sheet to fund operations – SVB subsequently had to sell assets as their liabilities fell – we then see realised losses from buying securities at much higher prices.
-Short sellers/investor base – shorts had an eye on unrealised losses from the worsening asset quality for weeks – the selling accelerated when the CEO/CFO/CMO disclosed they’d sold a chunk of stock on 27 March – it was over when the SVB took a $1.8b hit on its AFS securities available for sale on Wednesday – management sold $21b of its $28b book and announced a $2.25b in equity/debt raising - investors knew with conviction that depositors were fleeing – who supports a raising when liabilities are falling – no one sensible, raising pulled
-The Fed - failing to know such a shift in rates would impact banks asset quality when its primary function is financial stability.
-Regulation - Basel 3 - banks being forced to buy govt paper against deposits - v low risk weighting (perhaps required a hedge
Hard to pinpoint this on one aspect IMO - I think there is a perfect storm going on – a lack of hedging of interest rate risk was clearly a dominant factor behind this. Top down this is a function of rapidly tightening monetary policy and the impact this had on both the asset quality and liability side of the balance sheet – we should recall SVBs model is not the same as others in the banking space, so its hard to say this is systemic – still we wait for the outcome on next steps on how deposits over $250k will be dealt with – we’re hearing they may get 50% back initially but a buyer would be the best solution
The issue for regional/smaller banks comes if is we see some sort of haircut on the deposits claim over $250k – that could see a loss of confidence in holding deposits with other smaller banks names – we shall hear more soon, but broad contagion through the financial system seems unlikely, but it is a possibility given nearly 1/3 deposits in the banking system are uninsured – any bank with a large asset base and low equity are in the spotlight
As said Friday this could be a nothing burger or have real impactions on economics - the big issue happens this week if we see no clarity on how depositors are dealt (seems unlikely) with and we get a hot CPI print
Global risk Warning CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. Between 74-89% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading in CFDs. You should consider whether you understand how CFD
Penafian
Maklumat dan penerbitan adalah tidak dimaksudkan untuk menjadi, dan tidak membentuk, nasihat untuk kewangan, pelaburan, perdagangan dan jenis-jenis lain atau cadangan yang dibekalkan atau disahkan oleh TradingView. Baca dengan lebih lanjut di Terma Penggunaan.
Global risk Warning CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. Between 74-89% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading in CFDs. You should consider whether you understand how CFD
Penafian
Maklumat dan penerbitan adalah tidak dimaksudkan untuk menjadi, dan tidak membentuk, nasihat untuk kewangan, pelaburan, perdagangan dan jenis-jenis lain atau cadangan yang dibekalkan atau disahkan oleh TradingView. Baca dengan lebih lanjut di Terma Penggunaan.