Macro-Sentiment Index Model (MSIM)
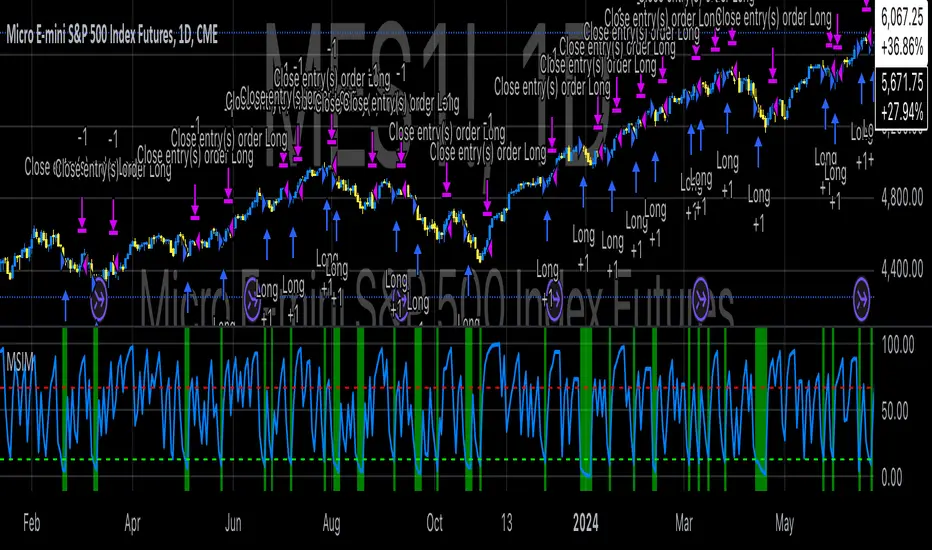
The MSIM utilizes a multi-faceted approach to measure sentiment. Drawing from the theory that macroeconomic variables can influence financial markets (Stock & Watson, 2002), the strategy incorporates market volatility (VIX), volume measures, and long-term market trends. These indicators help form a robust view of the market’s risk appetite and potential for price movement. For instance, high volatility often signals increased market uncertainty (Bollerslev, 1986), while volume-based indicators provide insights into investor conviction (Chen, 1991).
Additionally, the model incorporates macroeconomic proxies like GDP growth, interest rates, and unemployment data, leveraging the findings of macroeconomic studies that indicate a direct correlation between these factors and market performance (Hamilton, 1994). By normalizing these economic indicators, the model provides a standardized sentiment score that reflects the aggregated impact of these factors on the market’s outlook.
The MSIM aims to exploit market inefficiencies by responding to shifts in sentiment before they manifest in price movements. Studies have shown that sentiment indicators, such as the Advance-Decline Line and the Stock-Bond Ratio, can be predictive of future price movements (Neely, 2010). The model integrates these indicators into a single composite sentiment score, which is then filtered through momentum signals to refine entry points. This approach is grounded in behavioral finance theory, which suggests that investor sentiment plays a crucial role in driving asset prices, sometimes beyond the reach of fundamental data alone (Shiller, 2000).
The strategy is designed to identify long opportunities when sentiment is particularly favorable, with a focus on minimizing risk during adverse conditions. By analyzing market trends alongside macroeconomic signals, the MSIM helps traders stay aligned with the prevailing market forces.
References:
• Bollerslev, T. (1986). Generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity. Journal of Econometrics, 31(3), 307-327.
• Chen, S. S. (1991). The determinants of stock market liquidity. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 26(3), 283-305.
• Fleming, M. J., Kirby, C. W., & Ostdiek, B. (2001). The economic value of volatility timing. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 36(1), 113-134.
• Hamilton, J. D. (1994). Time series analysis. Princeton University Press.
• Neely, C. J. (2010). The behavior of exchange rates: A survey of recent empirical literature. International Finance Discussion Papers, 981.
• Shiller, R. J. (2000). Irrational Exuberance. Princeton University Press.
• Stock, J. H., & Watson, M. W. (2002). Macroeconomic forecasting using diffusion indexes. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 20(2), 147-162.
Skrip jemputan sahaja
Hanya pengguna disahkan oleh penulis boleh mengakses skrip ini. Anda perlu memohon dan mendapatkan kebenaran untuk menggunakannya. Keizinan selalunya diberikan selepas pembayaran. Untuk lebih butiran, ikuti arahan penulis di bawah atau hubungi EdgeTools secara terus.
TradingView TIDAK menyarankan pembayaran atau penggunaan skrip kecuali anda mempercayai sepenuhnya penulis dan memahami bagaimana ia berfungsi. Anda juga boleh menjumpai alternatif sumber terbuka dan percuma yang lain di dalam skrip komuniti kami.
Arahan penulis
edgetools.org
Penafian
Skrip jemputan sahaja
Hanya pengguna disahkan oleh penulis boleh mengakses skrip ini. Anda perlu memohon dan mendapatkan kebenaran untuk menggunakannya. Keizinan selalunya diberikan selepas pembayaran. Untuk lebih butiran, ikuti arahan penulis di bawah atau hubungi EdgeTools secara terus.
TradingView TIDAK menyarankan pembayaran atau penggunaan skrip kecuali anda mempercayai sepenuhnya penulis dan memahami bagaimana ia berfungsi. Anda juga boleh menjumpai alternatif sumber terbuka dan percuma yang lain di dalam skrip komuniti kami.
Arahan penulis
edgetools.org