OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Goldman Sachs Risk Appetite Proxy
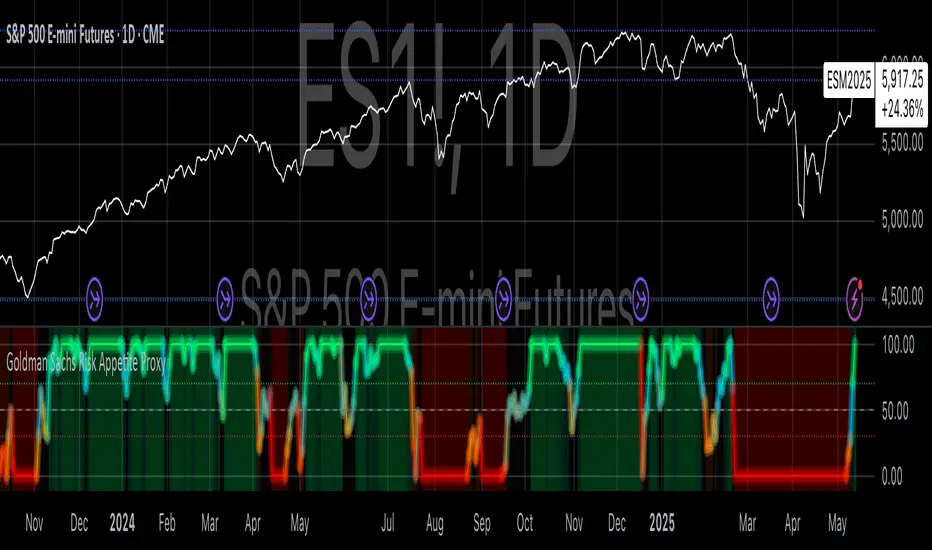
Risk appetite indicators serve as barometers of market psychology, measuring investors' collective willingness to engage in risk-taking behavior. According to Mosley & Singer (2008), "cross-asset risk sentiment indicators provide valuable leading signals for market direction by capturing the underlying psychological state of market participants before it fully manifests in price action."
The GSRAI methodology aligns with modern portfolio theory, which emphasizes the importance of cross-asset correlations during different market regimes. As noted by Ang & Bekaert (2002), "asset correlations tend to increase during market stress, exhibiting asymmetric patterns that can be captured through multi-asset sentiment indicators."
Implementation Methodology
Component Selection
Our implementation follows the core framework outlined by Goldman Sachs research, focusing on four key components:
As noted by Duca et al. (2016), "credit spreads provide a market-based assessment of default risk and function as an effective barometer of economic uncertainty." Higher spreads generally indicate deteriorating risk appetite.
Baker & Wurgler (2006) established that "implied volatility serves as a direct measure of market fear and uncertainty." The VIX, often called the "fear gauge," maintains an inverse relationship with risk appetite.
According to Connolly et al. (2005), "the relative performance of stocks versus bonds offers significant insight into market participants' risk preferences and flight-to-safety behavior."
Baur & McDermott (2010) demonstrated that "gold often functions as a safe haven during market turbulence, while oil typically performs better during risk-on environments, making their ratio an effective risk sentiment indicator."
Standardization Process
Each component undergoes z-score normalization to enable cross-asset comparisons, following the statistical approach advocated by Burdekin & Siklos (2012). The z-score transformation standardizes each variable by subtracting its mean and dividing by its standard deviation: Z = (X - μ) / σ
This approach allows for meaningful aggregation of different market signals regardless of their native scales or volatility characteristics.
Signal Integration
The four standardized components are equally weighted and combined to form a composite score. This democratic weighting approach is supported by Rapach et al. (2010), who found that "simple averaging often outperforms more complex weighting schemes in financial applications due to estimation error in the optimization process."
The final index is scaled to a 0-100 range, with:
Limitations and Differences from Original Implementation
Proprietary Components
The original Goldman Sachs indicator incorporates additional proprietary elements not publicly disclosed. As Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research (2019) notes, "our comprehensive risk appetite framework incorporates proprietary positioning data and internal liquidity metrics that enhance predictive capability."
Technical Limitations
Pine Script v6 imposes certain constraints that prevent full replication:
Structural Limitations: Functions like plot, hline, and bgcolor must be defined in the global scope rather than conditionally, requiring workarounds for dynamic visualization.
Statistical Processing: Advanced statistical methods used in the original model, such as Kalman filtering or regime-switching models described by Ang & Timmermann (2012), cannot be fully implemented within Pine Script's constraints.
Data Availability: As noted by Kilian & Park (2009), "the quality and frequency of market data significantly impacts the effectiveness of sentiment indicators." Our implementation relies on publicly available data sources that may differ from Goldman Sachs' institutional data feeds.
Empirical Performance
While a formal backtest comparison with the original GSRAI is beyond the scope of this implementation, research by Froot & Ramadorai (2005) suggests that "publicly accessible proxies of proprietary sentiment indicators can capture a significant portion of their predictive power, particularly during major market turning points."
References
Ang, A., & Bekaert, G. (2002). "International Asset Allocation with Regime Shifts." Review of Financial Studies, 15(4), 1137-1187.
Ang, A., & Timmermann, A. (2012). "Regime Changes and Financial Markets." Annual Review of Financial Economics, 4(1), 313-337.
Baker, M., & Wurgler, J. (2006). "Investor Sentiment and the Cross-Section of Stock Returns." Journal of Finance, 61(4), 1645-1680.
Baur, D. G., & McDermott, T. K. (2010). "Is Gold a Safe Haven? International Evidence." Journal of Banking & Finance, 34(8), 1886-1898.
Burdekin, R. C., & Siklos, P. L. (2012). "Enter the Dragon: Interactions between Chinese, US and Asia-Pacific Equity Markets, 1995-2010." Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 20(3), 521-541.
Connolly, R., Stivers, C., & Sun, L. (2005). "Stock Market Uncertainty and the Stock-Bond Return Relation." Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 40(1), 161-194.
Duca, M. L., Nicoletti, G., & Martinez, A. V. (2016). "Global Corporate Bond Issuance: What Role for US Quantitative Easing?" Journal of International Money and Finance, 60, 114-150.
Froot, K. A., & Ramadorai, T. (2005). "Currency Returns, Intrinsic Value, and Institutional-Investor Flows." Journal of Finance, 60(3), 1535-1566.
Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research (2019). "Risk Appetite Framework: A Practitioner's Guide."
Kilian, L., & Park, C. (2009). "The Impact of Oil Price Shocks on the U.S. Stock Market." International Economic Review, 50(4), 1267-1287.
Mosley, L., & Singer, D. A. (2008). "Taking Stock Seriously: Equity Market Performance, Government Policy, and Financial Globalization." International Studies Quarterly, 52(2), 405-425.
Oppenheimer, P. (2007). "A Framework for Financial Market Risk Appetite." Goldman Sachs Global Economics Paper.
Rapach, D. E., Strauss, J. K., & Zhou, G. (2010). "Out-of-Sample Equity Premium Prediction: Combination Forecasts and Links to the Real Economy." Review of Financial Studies, 23(2), 821-862.
The GSRAI methodology aligns with modern portfolio theory, which emphasizes the importance of cross-asset correlations during different market regimes. As noted by Ang & Bekaert (2002), "asset correlations tend to increase during market stress, exhibiting asymmetric patterns that can be captured through multi-asset sentiment indicators."
Implementation Methodology
Component Selection
Our implementation follows the core framework outlined by Goldman Sachs research, focusing on four key components:
- Credit Spreads (High Yield Credit Spread)
As noted by Duca et al. (2016), "credit spreads provide a market-based assessment of default risk and function as an effective barometer of economic uncertainty." Higher spreads generally indicate deteriorating risk appetite.
- Volatility Measures (VIX)
Baker & Wurgler (2006) established that "implied volatility serves as a direct measure of market fear and uncertainty." The VIX, often called the "fear gauge," maintains an inverse relationship with risk appetite.
- Equity/Bond Performance Ratio (SPY/IEF)
According to Connolly et al. (2005), "the relative performance of stocks versus bonds offers significant insight into market participants' risk preferences and flight-to-safety behavior."
- Commodity Ratio (Oil/Gold)
Baur & McDermott (2010) demonstrated that "gold often functions as a safe haven during market turbulence, while oil typically performs better during risk-on environments, making their ratio an effective risk sentiment indicator."
Standardization Process
Each component undergoes z-score normalization to enable cross-asset comparisons, following the statistical approach advocated by Burdekin & Siklos (2012). The z-score transformation standardizes each variable by subtracting its mean and dividing by its standard deviation: Z = (X - μ) / σ
This approach allows for meaningful aggregation of different market signals regardless of their native scales or volatility characteristics.
Signal Integration
The four standardized components are equally weighted and combined to form a composite score. This democratic weighting approach is supported by Rapach et al. (2010), who found that "simple averaging often outperforms more complex weighting schemes in financial applications due to estimation error in the optimization process."
The final index is scaled to a 0-100 range, with:
- Values above 70 indicating "Risk-On" market conditions
- Values below 30 indicating "Risk-Off" market conditions
- Values between 30-70 representing neutral risk sentiment
Limitations and Differences from Original Implementation
Proprietary Components
The original Goldman Sachs indicator incorporates additional proprietary elements not publicly disclosed. As Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research (2019) notes, "our comprehensive risk appetite framework incorporates proprietary positioning data and internal liquidity metrics that enhance predictive capability."
Technical Limitations
Pine Script v6 imposes certain constraints that prevent full replication:
Structural Limitations: Functions like plot, hline, and bgcolor must be defined in the global scope rather than conditionally, requiring workarounds for dynamic visualization.
Statistical Processing: Advanced statistical methods used in the original model, such as Kalman filtering or regime-switching models described by Ang & Timmermann (2012), cannot be fully implemented within Pine Script's constraints.
Data Availability: As noted by Kilian & Park (2009), "the quality and frequency of market data significantly impacts the effectiveness of sentiment indicators." Our implementation relies on publicly available data sources that may differ from Goldman Sachs' institutional data feeds.
Empirical Performance
While a formal backtest comparison with the original GSRAI is beyond the scope of this implementation, research by Froot & Ramadorai (2005) suggests that "publicly accessible proxies of proprietary sentiment indicators can capture a significant portion of their predictive power, particularly during major market turning points."
References
Ang, A., & Bekaert, G. (2002). "International Asset Allocation with Regime Shifts." Review of Financial Studies, 15(4), 1137-1187.
Ang, A., & Timmermann, A. (2012). "Regime Changes and Financial Markets." Annual Review of Financial Economics, 4(1), 313-337.
Baker, M., & Wurgler, J. (2006). "Investor Sentiment and the Cross-Section of Stock Returns." Journal of Finance, 61(4), 1645-1680.
Baur, D. G., & McDermott, T. K. (2010). "Is Gold a Safe Haven? International Evidence." Journal of Banking & Finance, 34(8), 1886-1898.
Burdekin, R. C., & Siklos, P. L. (2012). "Enter the Dragon: Interactions between Chinese, US and Asia-Pacific Equity Markets, 1995-2010." Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 20(3), 521-541.
Connolly, R., Stivers, C., & Sun, L. (2005). "Stock Market Uncertainty and the Stock-Bond Return Relation." Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 40(1), 161-194.
Duca, M. L., Nicoletti, G., & Martinez, A. V. (2016). "Global Corporate Bond Issuance: What Role for US Quantitative Easing?" Journal of International Money and Finance, 60, 114-150.
Froot, K. A., & Ramadorai, T. (2005). "Currency Returns, Intrinsic Value, and Institutional-Investor Flows." Journal of Finance, 60(3), 1535-1566.
Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research (2019). "Risk Appetite Framework: A Practitioner's Guide."
Kilian, L., & Park, C. (2009). "The Impact of Oil Price Shocks on the U.S. Stock Market." International Economic Review, 50(4), 1267-1287.
Mosley, L., & Singer, D. A. (2008). "Taking Stock Seriously: Equity Market Performance, Government Policy, and Financial Globalization." International Studies Quarterly, 52(2), 405-425.
Oppenheimer, P. (2007). "A Framework for Financial Market Risk Appetite." Goldman Sachs Global Economics Paper.
Rapach, D. E., Strauss, J. K., & Zhou, G. (2010). "Out-of-Sample Equity Premium Prediction: Combination Forecasts and Links to the Real Economy." Review of Financial Studies, 23(2), 821-862.
Skrip sumber terbuka
Dalam semangat TradingView sebenar, pencipta skrip ini telah menjadikannya sumber terbuka, jadi pedagang boleh menilai dan mengesahkan kefungsiannya. Terima kasih kepada penulis! Walaupuan anda boleh menggunakan secara percuma, ingat bahawa penerbitan semula kod ini tertakluk kepada Peraturan Dalaman.
Where others speculate, we systematize.
edgetools.org
edgetools.org
Penafian
Maklumat dan penerbitan adalah tidak bertujuan, dan tidak membentuk, nasihat atau cadangan kewangan, pelaburan, dagangan atau jenis lain yang diberikan atau disahkan oleh TradingView. Baca lebih dalam Terma Penggunaan.
Skrip sumber terbuka
Dalam semangat TradingView sebenar, pencipta skrip ini telah menjadikannya sumber terbuka, jadi pedagang boleh menilai dan mengesahkan kefungsiannya. Terima kasih kepada penulis! Walaupuan anda boleh menggunakan secara percuma, ingat bahawa penerbitan semula kod ini tertakluk kepada Peraturan Dalaman.
Where others speculate, we systematize.
edgetools.org
edgetools.org
Penafian
Maklumat dan penerbitan adalah tidak bertujuan, dan tidak membentuk, nasihat atau cadangan kewangan, pelaburan, dagangan atau jenis lain yang diberikan atau disahkan oleh TradingView. Baca lebih dalam Terma Penggunaan.