FunctionBaumWelch
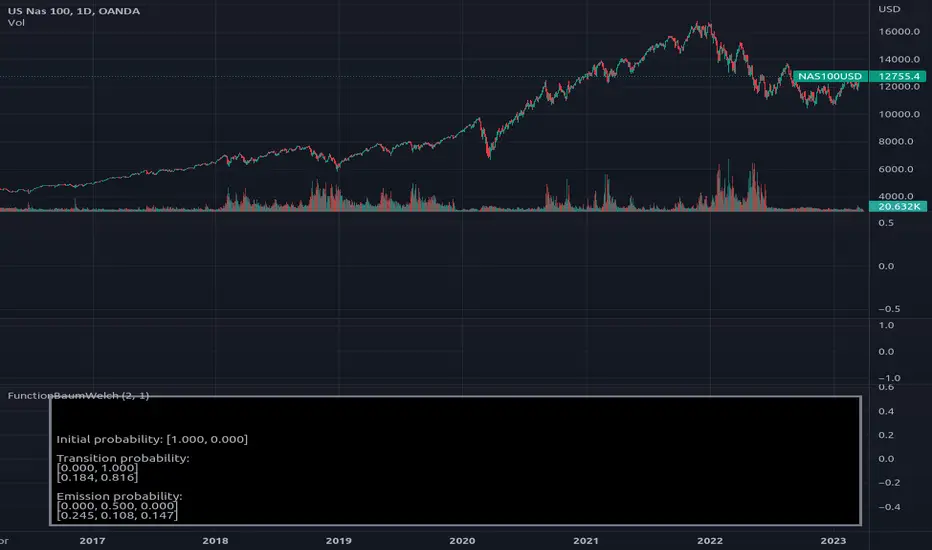
Baum-Welch Algorithm, also known as Forward-Backward Algorithm, uses the well known EM algorithm
to find the maximum likelihood estimate of the parameters of a hidden Markov model given a set of observed
feature vectors.
---
### Function List:
> `forward (array<float> pi, matrix<float> a, matrix<float> b, array<int> obs)`
> `forward (array<float> pi, matrix<float> a, matrix<float> b, array<int> obs, bool scaling)`
> `backward (matrix<float> a, matrix<float> b, array<int> obs)`
> `backward (matrix<float> a, matrix<float> b, array<int> obs, array<float> c)`
> `baumwelch (array<int> observations, int nstates)`
> `baumwelch (array<int> observations, array<float> pi, matrix<float> a, matrix<float> b)`
---
### Reference:
> en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baum–Welch_algorithm
> github.com/alexsosn/MarslandMLAlgo/blob/4277b24db88c4cb70d6b249921c5d21bc8f86eb4/Ch16/HMM.py
> en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Forward_algorithm
> rdocumentation.org/packages/HMM/versions/1.0.1/topics/forward
> rdocumentation.org/packages/HMM/versions/1.0.1/topics/backward
forward(pi, a, b, obs)
Computes forward probabilities for state `X` up to observation at time `k`, is defined as the
probability of observing sequence of observations `e_1 ... e_k` and that the state at time `k` is `X`.
Parameters:
pi (float[]): Initial probabilities.
a (matrix<float>): Transmissions, hidden transition matrix a or alpha = transition probability matrix of changing
states given a state matrix is size (M x M) where M is number of states.
b (matrix<float>): Emissions, matrix of observation probabilities b or beta = observation probabilities. Given
state matrix is size (M x O) where M is number of states and O is number of different
possible observations.
obs (int[]): List with actual state observation data.
Returns: - `matrix<float> _alpha`: Forward probabilities. The probabilities are given on a logarithmic scale (natural logarithm). The first
dimension refers to the state and the second dimension to time.
forward(pi, a, b, obs, scaling)
Computes forward probabilities for state `X` up to observation at time `k`, is defined as the
probability of observing sequence of observations `e_1 ... e_k` and that the state at time `k` is `X`.
Parameters:
pi (float[]): Initial probabilities.
a (matrix<float>): Transmissions, hidden transition matrix a or alpha = transition probability matrix of changing
states given a state matrix is size (M x M) where M is number of states.
b (matrix<float>): Emissions, matrix of observation probabilities b or beta = observation probabilities. Given
state matrix is size (M x O) where M is number of states and O is number of different
possible observations.
obs (int[]): List with actual state observation data.
scaling (bool): Normalize `alpha` scale.
Returns: - #### Tuple with:
> - `matrix<float> _alpha`: Forward probabilities. The probabilities are given on a logarithmic scale (natural logarithm). The first
dimension refers to the state and the second dimension to time.
> - `array<float> _c`: Array with normalization scale.
backward(a, b, obs)
Computes backward probabilities for state `X` and observation at time `k`, is defined as the probability of observing the sequence of observations `e_k+1, ... , e_n` under the condition that the state at time `k` is `X`.
Parameters:
a (matrix<float>): Transmissions, hidden transition matrix a or alpha = transition probability matrix of changing states
given a state matrix is size (M x M) where M is number of states
b (matrix<float>): Emissions, matrix of observation probabilities b or beta = observation probabilities. given state
matrix is size (M x O) where M is number of states and O is number of different possible observations
obs (int[]): Array with actual state observation data.
Returns: - `matrix<float> _beta`: Backward probabilities. The probabilities are given on a logarithmic scale (natural logarithm). The first dimension refers to the state and the second dimension to time.
backward(a, b, obs, c)
Computes backward probabilities for state `X` and observation at time `k`, is defined as the probability of observing the sequence of observations `e_k+1, ... , e_n` under the condition that the state at time `k` is `X`.
Parameters:
a (matrix<float>): Transmissions, hidden transition matrix a or alpha = transition probability matrix of changing states
given a state matrix is size (M x M) where M is number of states
b (matrix<float>): Emissions, matrix of observation probabilities b or beta = observation probabilities. given state
matrix is size (M x O) where M is number of states and O is number of different possible observations
obs (int[]): Array with actual state observation data.
c (float[]): Array with Normalization scaling coefficients.
Returns: - `matrix<float> _beta`: Backward probabilities. The probabilities are given on a logarithmic scale (natural logarithm). The first dimension refers to the state and the second dimension to time.
baumwelch(observations, nstates)
**(Random Initialization)** Baum–Welch algorithm is a special case of the expectation–maximization algorithm used to find the
unknown parameters of a hidden Markov model (HMM). It makes use of the forward-backward algorithm
to compute the statistics for the expectation step.
Parameters:
observations (int[]): List of observed states.
nstates (int)
Returns: - #### Tuple with:
> - `array<float> _pi`: Initial probability distribution.
> - `matrix<float> _a`: Transition probability matrix.
> - `matrix<float> _b`: Emission probability matrix.
---
requires: `import RicardoSantos/WIPTensor/2 as Tensor`
baumwelch(observations, pi, a, b)
Baum–Welch algorithm is a special case of the expectation–maximization algorithm used to find the
unknown parameters of a hidden Markov model (HMM). It makes use of the forward-backward algorithm
to compute the statistics for the expectation step.
Parameters:
observations (int[]): List of observed states.
pi (float[]): Initial probaility distribution.
a (matrix<float>): Transmissions, hidden transition matrix a or alpha = transition probability matrix of changing states
given a state matrix is size (M x M) where M is number of states
b (matrix<float>): Emissions, matrix of observation probabilities b or beta = observation probabilities. given state
matrix is size (M x O) where M is number of states and O is number of different possible observations
Returns: - #### Tuple with:
> - `array<float> _pi`: Initial probability distribution.
> - `matrix<float> _a`: Transition probability matrix.
> - `matrix<float> _b`: Emission probability matrix.
---
requires: `import RicardoSantos/WIPTensor/2 as Tensor`
Perpustakaan Pine
Dalam semangat sebenar TradingView, penulis telah menerbitkan kod Pine ini sebagai perpustakaan sumber terbuka supaya pengaturcara Pine lain dari komuniti kami boleh menggunakannya semula. Sorakan kepada penulis! Anda juga boleh menggunakan perpustakaan ini secara peribadi atau dalam penerbitan sumber terbuka lain, tetapi penggunaan semula kod ini dalam penerbitan adalah tertakluk kepada Peraturan Dalaman.
Penafian
Perpustakaan Pine
Dalam semangat sebenar TradingView, penulis telah menerbitkan kod Pine ini sebagai perpustakaan sumber terbuka supaya pengaturcara Pine lain dari komuniti kami boleh menggunakannya semula. Sorakan kepada penulis! Anda juga boleh menggunakan perpustakaan ini secara peribadi atau dalam penerbitan sumber terbuka lain, tetapi penggunaan semula kod ini dalam penerbitan adalah tertakluk kepada Peraturan Dalaman.